As a small business owner, you’re focused on providing a profitable product or service and achieving business growth, meaning more cash for you now plus a higher sale price in the future. Having accurate financial data is a priority for long term growth and success. One of the key financial indicators that lenders and investors evaluate are your retained earnings – that is – the way you manage annual profit reinvested in the business. Retained earnings are recorded on your balance sheet as a line item for each accounting period.
Once your business begins to earn a profit, cash flow forecasting will enable you to plan for the future. Having a BooksTime bookkeeper to analyse your financials means that we will be looking at your retained earnings and net profit (revenue and income streams minus expenses) remaining after dividends paid at the end of each reporting period. The retained earnings formula is the calculation used to determine the balance in the retained earnings account on your financial statement. Retained earnings have the power to fund growth opportunities such as working capital, or they may be reinvested in the company to fund Research and Development (R&D), invest in marketing, pay off debt or purchase new equipment.
Why is it important to utilise the retained earnings formula to track your retained earnings on your financial statements?
The way you manage your net profit over time – particularly retained earnings – is an important consideration for potential lenders and investors. Your statement of retained earnings is vital when applying for a loan or investment funding because it gives investors insight into how healthy your business is and what your business intentions are. Positive retained earnings indicate a commitment to overall growth whereas negative retained earnings are indicative of net loss and an accumulative deficit.
If you are a sole proprietor, your accountant may not have created a statement of retained earnings for you because retained earnings for your small business will appear on your financial statement as equity, (retained earnings, plus the sum of your inventory and assets, minus liabilities). However, a statement of retained earnings based on the retained earnings formula is an essential marker of your business’s health and can work in your favour in attracting potential lenders and investors. At BooksTime, we don’t just organise your financial data, we create user-friendly reports and statements to help you track the specific metrics that matter to you. Our cash flow forecasts empower you to plan for the future, and when you need a compelling retained earnings statement (calculating retained earnings) for investors or lenders, we’ve got your back.
What about tax liabilities? A company pays tax on its annual net income, not on retained earnings. When net profit is distributed as dividends paid, shareholders are liable for tax incurred on income.
Before we dive into the formula for calculation of retained earnings, let’s review some terms that are used in this formula. The first term is net income. Many people who are far from business consider “profit” and “income” to be synonyms. There is the logic here(where rent is, there is perhaps profit), but a person engaged in business should understand the difference between these concepts.
Net income (net profit) refers to all the revenues and other income streams that an individual, or legal entity, state or organization receives during a specific period minus all expenses that the business had. These expenses will include operating expenses, manufacturing expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest paid, taxes, etc. In other words, net income includes all the cash flows in and out of the company.
Profit is a financial result. In other words, these are funds that remain with the individual/legal entity after the costs of goods sold is deducted from the amount received as a result of the sale of the product or service. One can also calculate operating profit by even subtracting operating expenses. So, back to the definitions. Net income is the difference between revenue (i.e., income) and all possible costs. Profit is all money received by an entrepreneur/enterprise for any period minus some expenses, such as cost of goods sold.
Dividends are another item in the formula. Bonuses are payments that shareholders receive at the expense of the net profit of the corporation based on the results of its work and depending on the number and types of shares owned by them. The source of dividends is the company’s profit from economic activities, and the form of payment is cash. Amount using the property of the company is possible if such a method is provided for by the charter. An essential body decides to pay dividends of the corporation – the general meeting of shareholders.
How to use the retained earnings formula to achieve maximum net income and sustained business growth
It’s important to note that at BooksTime, we understand that your focus is building your business, developing and selling your product/service and establishing your brand identity in a highly competitive market in the United States, or even on a global scale. It can be difficult to find the time to analyze your financial data. If you’re not in the accounting or financial sector, you might not be interested in tracking your cash flow or reading your balance sheet and that’s okay! We’ve got you covered.
The retained earnings formula calculates the dollar value of funds at your disposal after taking into consideration mandatory payments for the reporting period. To make use of this formula, we need to define the following terms as per listed below.
1.Net Income / Net Profit
Firstly, it should be noted that the terms ‘net income’ and ‘net profit’ can be used interchangeably; whilst in an accounting context, the usage of the two terms differs slightly. Essentially, both terms refer to all revenue and income streams received during the reporting period, minus expenses and both refer to positive cash flow on the cash flow statement. Technically, net income is a form of profit, as it refers to the resulting figure of revenue, including expenses such as cost of goods sold (COGS), operating costs, payment of debt, interest on loans and accrued from investments, additional income streams from the sale of assets or from subsidiary holdings, depreciation and amortization of assets and taxes. As net income is a figure reported on your income statement, it’s, therefore, able to be manipulated through aggressive accounting policies.
Net profit, on the other hand, is an income statement’s bottom line. It is a financial result. Gross profit is the figure that remains after the cost of goods sold (COGS). Operating profit refers to revenue minus cost of goods and operating expenses. Therefore, when we look at the accounting definitions of ‘net income’ and ‘net profit’:
- Net income refers to the revenue a business makes during a given period, minus all expenses.
- Net profit refers to income received by a business during a given period, minus cost of goods sold (COGS) and/or operating expenses.
2. Dividends Paid
Before we look at how to calculate retained earnings utilizing the retained earnings formula, we need to define ‘dividends paid’. A business owner may wish to distribute dividends to its shareholders and investors based on the business’s performance during a reporting period. Dividends are paid from net profit and affect the balance of the retained earnings account.
Now that we have defined the terms: ‘net profit’ / ‘net income’ and ‘dividends paid’, we can assess how the retained earnings formula can work for you to assist you in understanding your cash flow statement, planning for future business growth and maximizing your business’s profit.
GET A FREE REVIEW OF YOUR BOOKS TODAY
The retained earnings formula
If you are utilising automated accounting software, and all income and expenses have been recorded correctly by an experienced bookkeeper, it will be easy for you to view reports on retained earnings, as well as more general statements that include this information, such as the Balance Sheet.
Retained earnings are calculated by starting with the prior reporting period’s retained earnings balance, adding the sum of net profit/loss and subtracting dividends paid.
The basic retained earnings formula is RE 1 = RE 0 + NI – D
- RE 1 – net income at the end of the reporting period
- RE 0 – net income at the beginning of the period
- NI – net income minus income tax
- D – Dividends paid
So, how can this formula help you to achieve maximum net income and sustained business growth? Choosing to focus on long-term business growth is a mindset, and making the decision to reinvest rather than taking profits as a distribution enables you to invest in:
- Working capital
- Equipment purchases
- Research and development
- Marketing
- Repaying debt
Retained earnings are cumulative, meaning that they’re reported on your balance sheet in the equity section, and RE 0 is carried over from the retained earnings of the previous reporting period. Making use of the retained earnings formula to ascertain your business’s capacity to retain earnings makes you more attractive to lenders and investors in the long term by displaying in hard print your business commitment to the overall growth and development of your organization.
How does Common Stock affect Retained Earnings?

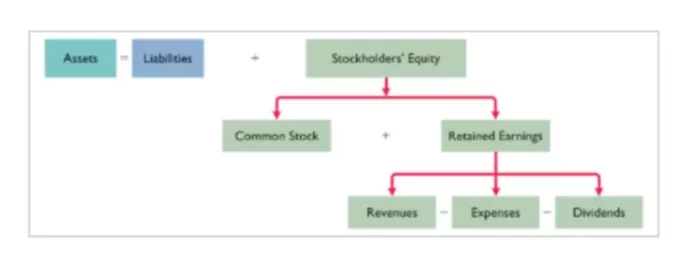
The balance sheet incorporates assets = sum of liabilities and stockholder equity, (or, as the formula is commonly known, assets=liabilities). Stockholder equity comprises common stock and retained earnings. Common stockholders collect dividends, which decreases the accumulated earnings of a company however, the sale of common stock does not itself affect retained earnings.
BooksTime can help you to understand your retained earnings and your business’s cashflow
Your BooksTime bookkeeper won’t only help you to manage your financial data, they’ll also help you to understand and use your data to grow your business. We understand that whilst you know that the retained earnings formula is important, taking the time to understand it isn’t a priority because the content can be dry or uninteresting. Your priority as a business owner is in growing your business and that involves focusing on your specialization. Let us take the hard work out of interpreting financial data and using it to obtain strong and consistent business growth. We can provide you with:
- Monthly reports to give you a clear and accurate view of your finances.
- The ability to track trends that matter to you most with customised visual dashboards.
- Customised cash flow forecasts to assist you to plan for the future.
- High level consulting finance guidance to provide you with financial leadership, help you to design a financial strategy, prepare presentations to impress prospective lenders and investors and advise on M&A initiatives.
If you have any questions about retained earnings or the retained earnings formula, or if you would like to book a free consultation with us, complete this form and we’ll be in contact with you within 24 hours.

















