Non-manufacturing overhead costs, also simply referred to as non-manufacturing costs, are costs not related to production. comes from. You might also see them known as period costs. They are divided into categories known as Selling or General and Administrative. Companies can choose to just have one big SG&A category or break it out into separate categories.
- Marketing or selling costs – when we think about the selling component of the SG&A, we are really talking about the costs to get orders (some people refer to them as order getting costs or ordering filling costs) and get that order to the customer. They include things like advertising and sales salaries and commissions as well as the product shipping to the customer.
- General and administrative costs –With general and administrative costs, we are talking about costs that are required to run an organization, but they do not necessarily fall into marketing and they are definitely not manufacturing costs. This includes costs associated with the general management, executive compensation, CEO salary, manager’s salary and other people who are not involved with selling or manufacturing, but they help to manage the organization. These people can also be doing accounting, legal work, or public relations.
Non-Manufacturing Costs in the Financial Statements
Unlike costs that are directly associated with manufacturing and go through the Inventory accounts first, then the Balance Sheet and only afterward the Profit and Loss Statement, non-manufacturing overhead costs are accounted for as an expense in the period incurred. The expenses, accordingly, fall within the Income Statement in the financial statements. It is pretty straightforward – if we pay the accounting department a salary, those costs are expensed immediately.
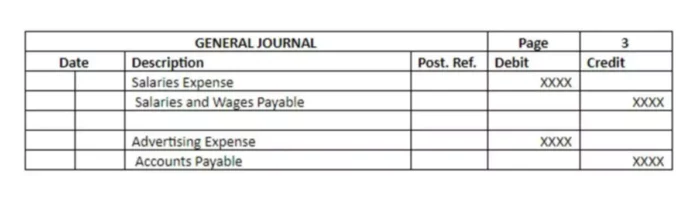
Non-manufacturing costs would be recorded in the journal as shown below.
Allocation of Non-Manufacturing Overhead Costs
In financial accounting, only manufacturing costs are allocated by type of product. As said before, these costs are considered as expenses for the reporting period and are treated in the same way as overstatement or underestimation of manufacturing overhead costs.
For external reports, therefore, it is not necessary to distribute non-manufacturing overhead costs by type of product. However, this may be required for decision making. For example, in many organizations, it is common practice to set sales prices based on estimates of total costs or even based on actual costs.


















