Financial statements Definition
The term financial statements refer to four accounting reports. In financial accounting, we have four financial statements. Accountants typically prepare them in the following order:
- Profit and Loss Statement
- Statement of Retained Earnings
- Balance Sheet
- Statement of Cash Flows
Financial statements are a window into the corporate world. We use financial statements for the following goals:
- To measure the profitability of companies;
- To figure out why companies are profitable and whether that profitability is sustainable;
- To measure the financial strength of companies. We want to know how much equity capital there is in there and how much borrowing is doing.
All of that gives as an accounting model, which is regulated by the GAAP rules. The data is there for us to use, so we must make sure we use it. Businesses entity can compile financial statements at any time during the year. Commonly, they are prepared at the end of the year (annual reports) or monthly or every three months (quarterly reports). Businesses can also choose any date for the end of their accounting (or fiscal) year.
Four Types of Financial Statements
- Balance Sheet
This report shows the financial condition of the company as of a particular date. It is an itemized statement that summarizes the assets and liabilities of a business has on a given date, usually at the end of the financial year. This is the company’s report card.
- Income Statement
This report shows the total amount of sales, all costs incurred in achieving them and other operating costs. It is an accounting of business transactions: revenue, expenses, and earnings. This helps to see if the company has recorded a profit for that particular month or another period.
- Statement of Cash Flow
This is a statement of the cash a company generates and how it does it. In many cases, while a transaction occurs, it is not recorded on the income statement. In such cases, it is put in the statement of cash flow. For example, a loan that is taken and kept aside for later use. This statement records this cash transaction.
- Retained Earnings Statement
Retained earnings is a proportion of profit kept in the business after declaring the dividends. This report reflects the cumulative profits or earnings of a firm after paying the dividend.
Link between Financial Statements
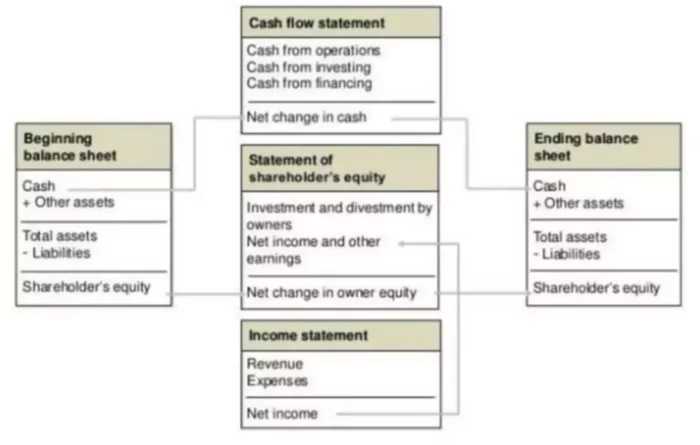
A picture above illustrates the connection between the common reports. For example, here is an explanation of the links between Income Statement and Income Statement:
- Assets used to generate cash flow and revenue. For a hospitality business, this is land, building, and equipment.
- Expenses are related to liabilities, e.g., accrued wages and accounts payable.
- Retained earnings will increase with net income, less any dividend payments.
Learn more about consolidated financial statements in our blog.

















