Bookkeeping in its essence is the activity of keeping a record of economic activities transactions of a company in a documentary form. It facilitates the management of economic activities, payment of salaries, calculation and payment of taxes, and other mandatory cash payments.
The head of the business or a private entrepreneur should take care of the bookkeeping. They can independently record information on transactions in the book of accounts and draw up documentation, hire an employee for this, or entrust bookkeeping to an outsourcing company.
Bookkeeping and accounting are strictly regulated by the current legislation, so intentional or unintentional errors and inaccuracies in the financial book may entail legal responsibility within the framework of the current administrative and criminal legislation. However, in reality, bookkeeping is not as scary as it seems to inexperienced bookkeepers. Let’s consider what business bookkeeping is in simple words and see how it relates to accounting.
What is Bookkeeping in Simple Words?
Bookkeeping is an orderly system for collecting, keeping a record of and summarizing transactions and other financial information in monetary terms about the property, obligations of the business, and their movement through continuous documentation of all business transactions on an accrual basis.
Any accounting transaction must be recorded in the general ledger. Buying a pencil with cash or on account, paying a salary, calculating depreciation, or obtaining a loan are all types of business transactions that must be recorded and reflected properly in their accounts. Each transaction must be documented by a bookkeeper (or accountant).
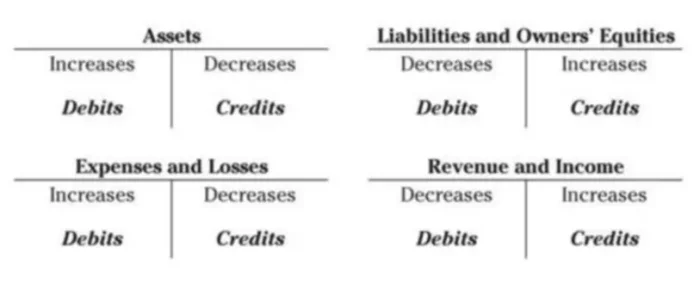
One of the main principles of bookkeeping is the reflection of all transactions using a special accounting book of accounts. Each transaction must be reflected on the debit and credit sides of the relevant bookkeeping accounts to maintain the accounting balance. Bookkeeping information is needed for those who make decisions and develop plans for the development of companies, as well as those who manage these companies. For example, business leaders use accounting information when deciding whether to:
- develop a new product or service (for example, a computer manufacturer may analyze this information and decide to develop a new line of computers)
- increase or decrease the price of its products, increase or decrease its production (for example, a marketing company may change its advertising plans)
- take out a loan to expand the business (for example, a reseller can take out a loan to expand its network of stores)
- increase or decrease production capacity (for example, a farm may change the size of its land plot)
- change methods of procurement, production or distribution (for example, a clothing manufacturer may change its local suppliers to overseas suppliers).
In addition, it helps to solve several tasks at once. For instance, a holistic picture of the financial and economic activities of an entity is drawn up; the expenditure side of economic activity is minimized to increase the profitability; search for reserves that allow improving the results without attracting additional funds; and compliance with applicable tax and other legislation is monitored.
The ultimate goal of bookkeeping is the formation of reliable records about the transactions, asset accounts, cash, earnings, debts to counterparties, etc. All financials are entered in bookkeeping accounts on an accrual basis and presented in annual financial statements.
The financial statements are intended for multiple purposes. Inside the company, the reporting data is analyzed by the director, founders, and auditors. Outside the business, they can be requested by banks for making a decision on granting a loan, investors to assess the feasibility of investments, and regulatory authorities.
Bookkeeping vs Accounting: What is the Differ
Are you one of many individuals who think bookkeeping and accounting mean the same thing? Although both cover some of the same concepts, they are applied differently in the accounting world. Below, you can see a comparison of both.
What Do You Need to Set Up Bookkeeping for Business
Formerly, bookkeeping and accounting were carried out manually by bookkeepers with the help of a physical book of accounts. Later, this process was simplified and accelerated through the use of counting machines and calculators. Nowadays, a bookkeeper does all the bookkeeping using accounting software and applications and most of the routine bookkeeper’s duties are automated.
There are several ways to establish bookkeeping and accrual-based accounting for your business.
- Hiring a bookkeeper/accountant. This is a good option in the case of a large amount of bookkeeping work. However, difficulties arise in finding a qualified and honest accountant, monitoring their work, and organizing a workplace.
- Part-time employee. The advantage of this option is the low labor costs. However, the quality of bookkeeping usually suffers, especially if a bookkeeper is responsible for a large volume of work.
- Outsourced bookkeeping. This is a relatively new, but quite effective option for organizing bookkeeping and accounting. Accounting services are provided by a special company, which is responsible for the correctness of the records.
Modern bookkeeping requires a tremendous amount of knowledge and experience. Moreover, it is dynamically changing due to the constant improvement of legislation, the adoption of new regulations, and amendments to old ones. Therefore, only a bookkeeper and accountant with special education can independently conduct bookkeeping and accounting tasks. However, there are basic concepts every business owner should be aware of when setting up accrual bookkeeping at their business.
Any business is a group of business processes. A business process is a collection of interrelated activities or work aimed at creating a specific product or service for consumers. There are three types of business processes:
- Management: processes that manage the functioning of the system.
- Operational: processes that constitute the main activity of the company and create the main stream of income.
- Supporting: processes that serve the core business, such as accounting, recruiting, technical support, administrative department.
Financial business processes in most companies are supporting or service processes. Their task is to help the functions of sales, production, logistics, supply, administration to generate maximum profits, wisely using the company’s working and fixed assets, that is, to facilitate the process of making money. To accomplish these tasks, the business needs to have bookkeeping properly set up.
For the appropriate record and organization of bookkeeping at the business, an accounting policy should also be developed. Your accounting policy can include other rules specific to your industry and your business.
As was mentioned, no one has been keeping accounting records manually for a long time. There are now many solutions on the market for automating bookkeeping as much as possible, so you can choose one that meets your preferences and needs the best. If you are not ready to pay for software and want to do everything yourself, you can start off by simply recording when cash is going out of your entity and when it is coming in.
For some, this is not sufficient and they want to use the double-entry method. In this case, you also need to create a list of all the accounts that you will use to record data on every transaction you make as part of your business. In a nutshell, whenever you add or subtract money from an account you’re using debits and credits.
At the end of the period, you would calculate the final balance for each account, check if the records in your books and bank account(s) coincide, and prepare reports that you can use to file your taxes and manage your business.
Understanding Liabilities, Equity and Assets When Balancing the Books
The main accounting document among financial statements is the Balance sheet. It is prepared by a business to convey an accurate reflection of the financial condition of the business. The main components of the Balance sheet would be assets owned by the business and money owed to other parties, as well as the presence of equity capital.
The document is created using the accounting equation that represents equality between the balance on asset accounts and the balance on liability accounts of the business. Assets include all property and resources of an economic entity. The liabilities reflect obligations before third parties, employees, suppliers, and owners.
The current assets on the Balance sheet are characterized as the most liquid. In the records of book of accounts, you will typically see transactions relating to:
- cash and cash equivalents
- materials, stocks involved in the production process
- short-term customer debts
- financial investments.
Resources, the duration of which exceeds the reporting period, are considered non-current or fixed.
Liability accounts are the company’s debt, which in turn is divided into the following categories:
- Long-term: the business debt accounts that exist for a long time (long-term loans, etc.).
- Short-term: an actively changing amount of debt during the tax period, such as business debts to suppliers, financial institutions, personnel, unearned revenue, and other obligations of a short-term nature.
In addition to liability accounts, there is another section on the liabilities side of this financial statement, which is the equity account. Often, the indicator is calculated as net assets, that is, the difference in the balance of other assets and liabilities of the enterprise. Equity accounts are a set of contributions from the founders and the retained earnings of the business.
Income Statement and Bookkeeping: Expenses, Costs and Revenue
An important document for every business is an Income statement, which demonstrates the net income of the business, as well as the calculation of this indicator. An accrual basis (not cash basis), that is, at the time when they were actually performed is typically adhered to when a bookkeeper has to record a transaction.
Revenue reflects the cash received sales transaction during the reporting year. The costs (COGS) line sums all costs directly related to the production of products/provision of services. Selling expenses are the expenses of a company associated with organizing sales. Selling expenses include transactions such as transportation costs, warehouse rental, salaries for personnel associated with the sale, marketing costs, etc.
Administrative expenses include a record of expenses associated with the administrative and management support of the company. They include utility costs, depreciation of fixed assets for general business purposes (for example, office buildings), expenses for legal and financial consulting services, other (security, office equipment, etc.).
In accounting records, all the business costs and expenses described above are also called the operating expenses of the business. Revenue less operating expenses is the company’s operating income. The financial income and costs are associated with the provision and receipt of financial services. Financial income includes interest on loans and credits issued, interest on deposits, etc. Financial expenses, in turn, include interest expense on finance lease, accrued dividends on shares, etc.
Other income and expenses comprise all income and expenses of a business that do not fall into any of the above categories. Income tax includes income tax expense incurred by a company in the reporting year. The net profit of a business is the accounting value that formally remains at the disposal of shareholders after settlements with counterparties, creditors, and the government.
The Bottom line
Taking into account everything mentioned in this guide, the main functions of bookkeeping and accounting at the company can be easily formulated:
- Control. Accounting control greatly facilitates control cash movements within the enterprise and between counterparties, the use of inventory items, the timeliness of settlements for various payment transactions.
- Statistics. From the bookkeeping data, you can obtain primary and summarized information on all accounts, which will serve as the basis for further operational and strategic management decisions. On their basis, it will be possible to plan further economic activities of the business.
- Analytics. Data collected by the bookkeeper can be used by an accountant to analyze the current position of the company in the market. The head of the company or heads of departments can identify bottlenecks, unprofitable areas of activity, find ways to optimize costs, etc.
As you can see, bookkeeping plays a key role in every business, so it is important that every cash and the non-cash transaction is recorded correctly and in a timely manner using the accrual method or cash method (if applicable).