Definition
Before proceeding to the preparation of management and financial reports, an Adjusted Trial Balance is prepared. For that, adjustment entries are made to the Unadjusted Trial Balance. The latter are necessary in order to ensure an accurate reflection as well as consistency of business income and expenses.
Adjusting accounting transactions are recorded last in the transaction log and transferred to the General ledger, after which an Adjusted Trial Balance is compiled. The debits and credits might increase or decrease compared to the Unadjusted Trial Balance due to adjusting accounting entries, but the balance should still be maintained.
Adjusting Entries
1) Accruals
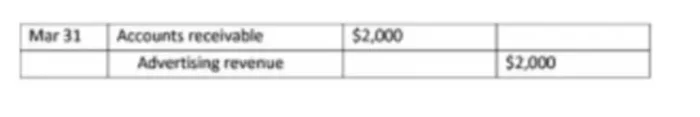
Accrued revenues are revenues earned, but not received in monetary terms, and therefore represent receivables. Accrued income is generated either after a certain period of time (for example, rent or interest) or in connection with the provision of services for which no invoices have been issued or funds have not been received.
Example: In March, an advertising agent rendered services worth $2,000 and will only be paid in April. On March 31, an adjusting accounting entry is drawn up:
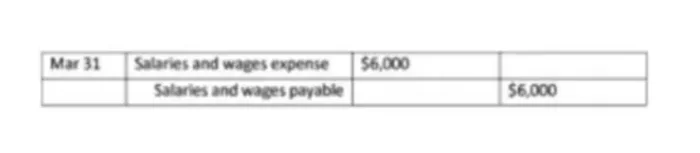
Accrued expenses – expenses incurred but not paid, i.e. represent the amount of liabilities.
Example: The salaries and wages of the company’s employees were $6,000 in the last week of March and will be paid out in April. On March 31, an adjusting accounting entry is drawn up:
2) Deferrals or prepayments
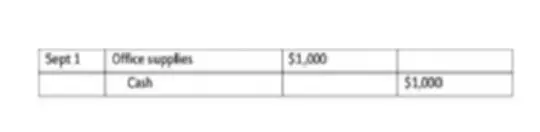
Prepaid expenses are the amounts of expenses paid, which are recorded as assets until the corresponding economic benefits are used or consumed, i.e. during the reporting period, cash was paid in advance for what will be consumed or used in subsequent periods and is considered business expenses. Along with this, the mentioned expenses relate to several accounting periods, and therefore should be distributed among them.
Example: A company bought $1,000 worth of office supplies on September 1. On September 30th, the inventory revealed that there was $600 worth of office supplies. It is necessary to create accounting entries for the purchase of office supplies, adjusting them as of September 30.
Deferred (unearned) revenues are revenues received that are included in liabilities until they are “earned”. Deferred revenue is “earned” upon delivery of goods or services to customers.
Example: Star Inc. will receive $6,000 from the tenant on September 1st for rent for the period from September to November inclusive. On September 30, an adjusting accounting entry is drawn up, registering the receipt of proceeds from the lease of property for September:
3) Estimated items
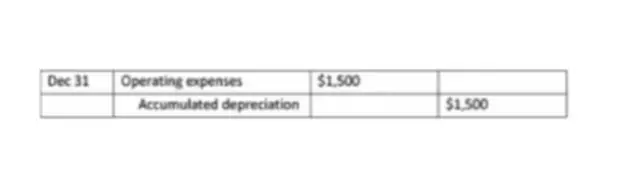
This type of adjustment entry is used when the amount of income or expenses that should be attributed to a given reporting period cannot be accurately determined (for example, depreciation of fixed assets).
Example: A company purchased equipment for $30,000 with a useful life of 20 years. It is necessary to account for depreciation expenses for equipment.